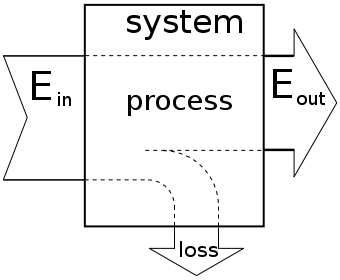
Energy system is a well-defined system in which energy flows enter the system to perform certain activities.
It can be converted into multiple forms (energy output) and according to the second law of thermodynamics, a fraction of it is always lost in the conversion process.It may represent, for example, a car engine, a house, a machine or the country’s energy system.In any energy system, we have some energy conversion process, which is the process of changing one form of energy to another.
The metric that measures the energy conversion efficiency is called the system efficiency.
Is the ratio between the Energy Output over the Energy Input. Remember that this value may be smaller than one (e.g. in thermal engines) or greater than one (e.g. in heat pump systems).
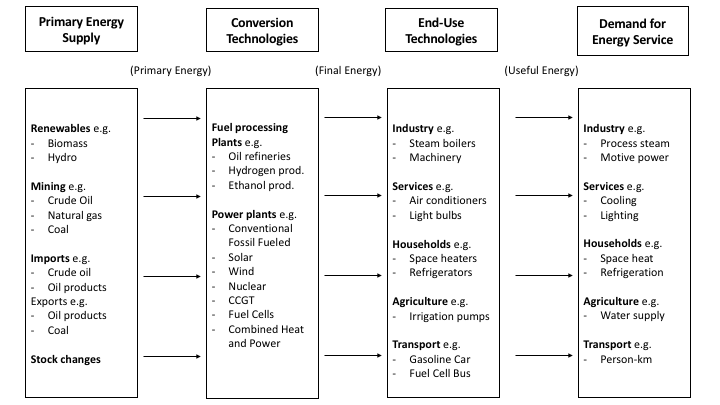
Reference Energy System
It is a representation of all of the technical activities required to supply various forms of energy to end-use activities.
An accounting framework for the compilation of data on all energy products entering, exiting and used within a system (e.g. the national territory of a given country) during a reference period.
It is a diagram that represents activities and the technologies and energy flows from primary energy supply to final energy use and eventually (though not as common) useful energy flows and energy services.
The reference energy system is a framework that helps to describe an energy system by describing the energy flows, the energy conversion technologies and the energy outputs.In practice, the reference energy system is a diagram that represents technologies and processes and the energy flows between these.
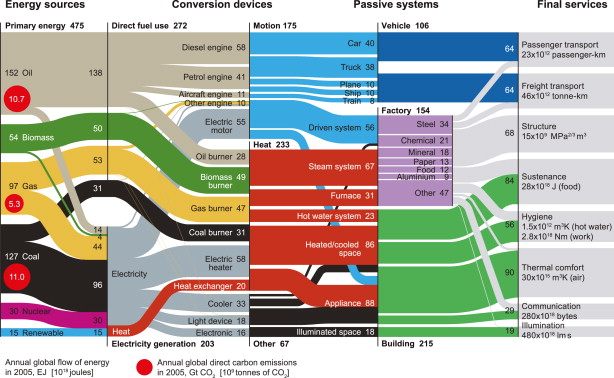
In particular, we introduce now three new concepts: the primary, final and useful energy.The breakdown of primary to final to useful energy is very relevant, because with each conversion step some energy is always lost.
Source: Jonathan M. Cullen, Engineering Fundamentals of Energy Efficiency, PhD Thesis, Cam, Figure 3.1 The flow-path of energy p. 49, available at: link
The design of an efficient energy system consists of avoiding unnecessary losses, we always aim at eliminating unnecessary steps in the flow of energy.
Primary energy is the energy embodied in natural resources which involve extraction, (e.g. oil and coal, but also wind and solar). Primary energy refers to energy sources as found in nature.
Final energy is the result of the transformation of primary energy sources the energy embodied in commodities which involve human transformation (e.g. electricity or gasoline or LPG) and it is usually, energy that is available at the consumer level.
Useful energy is the energy really spent at the end-use technologies. The portion of final energy which is actually available after final conversion to the consumer for the respective use (service). For example, depending on the technology conversion, electricity becomes (e.g. light, mechanical energy or heat).
Energy service Service that is provided by useful energy (E.g. light, mechanical energy or heat)
In the reference energy system, we can observe that on the left side we have the technologies and activities that enable us to collect primary energy (the primary energy supply area), like oil extraction, coal mining, biomass collection, etc. Then, the second area refers to conversion technologies from primary to final energy supply and its transportation, like electricity generation on power plants or oil refining. In some cases, like biomass or natural gas, the primary energy is consumed directly as a commodity (it means final energy) and there is no conversion process.
We have a second level of technologies which are the end-use technologies that allow us to change the final energy into a form of useful energy to perform different activities, like heating, mechanical movement or light, and these activities, which are not energy nor technologies, are the energy services. So, we present here the first definition of energy service that describes an activity that can be performed by means of useful energy.
Energy supply and the Energy demand
The energy supply Energy that is extracted from nature. It is basically all the activities that allow extraction, transportation and storage of fuels. Usually energy supply refers to primary energy vectors.
The energy demand Energy that is consumed by a particular system or economic sector. It is the energy required to provide the products and services and usually refers to final energy vectors. The energy demand may be described by technology (in the case of a building energy system) or by economic activity (in the case of a country’s energy system).
Energy Conversion Process that describes the conversion from primary to final (or final to useful).
Waste energy Energy lost in the conversion process.
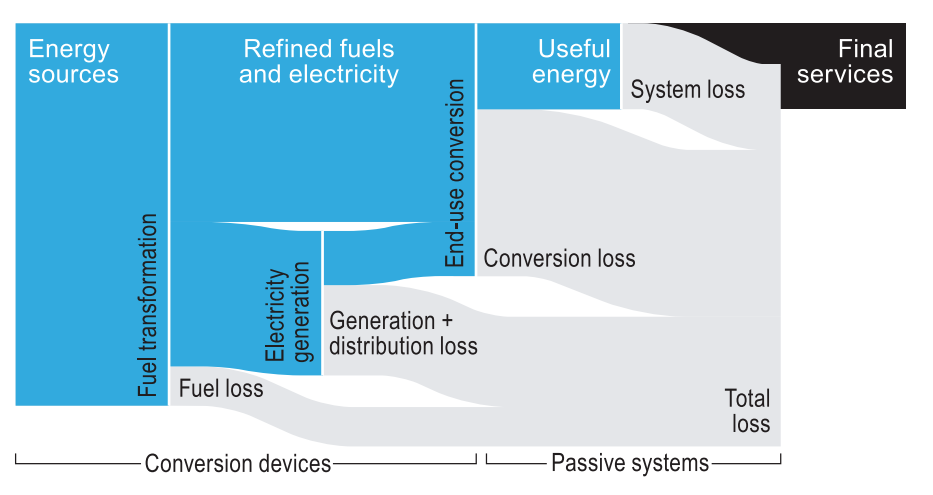
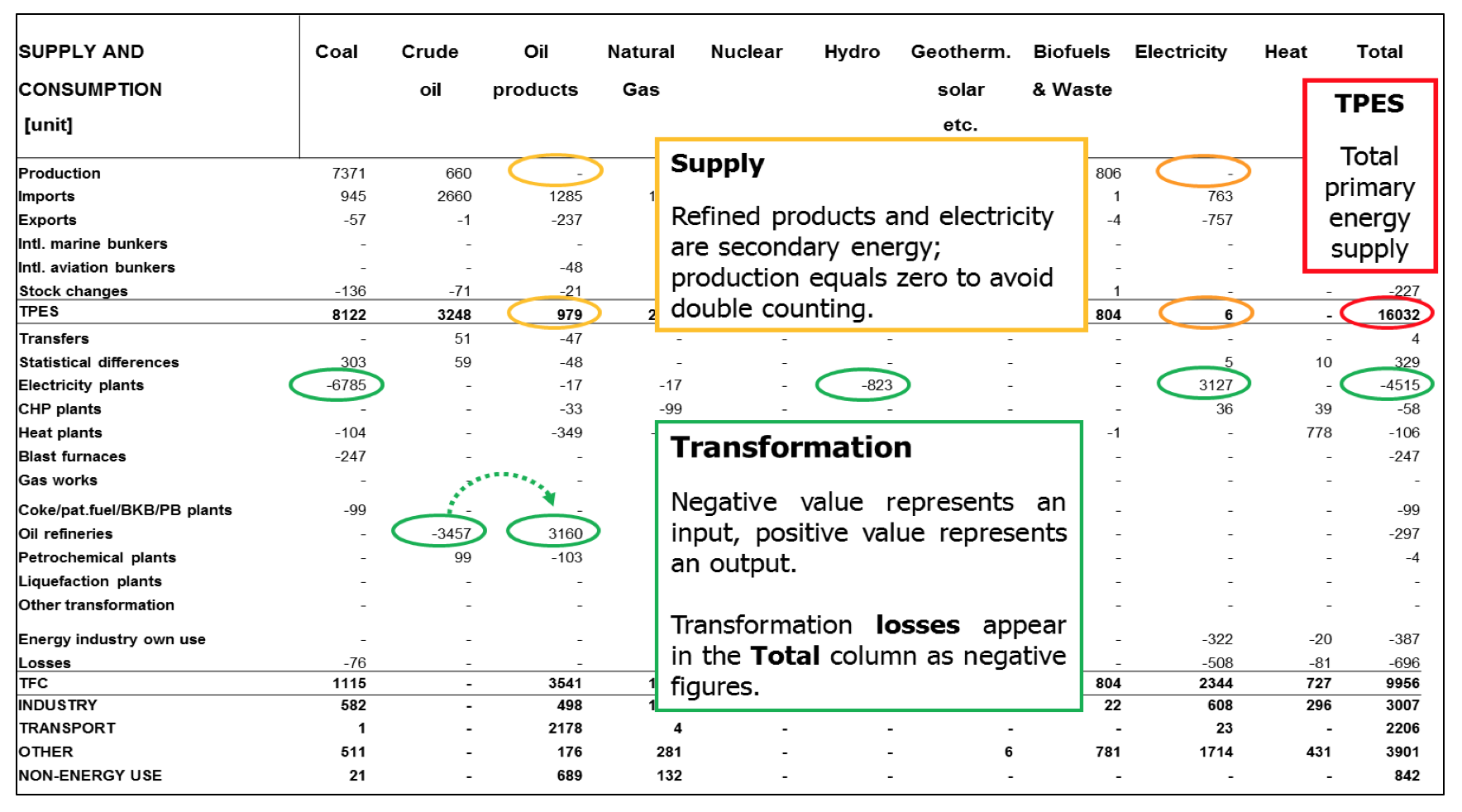 Source: EIA Global Headline Energy Data (2017 edition)
Source: EIA Global Headline Energy Data (2017 edition)